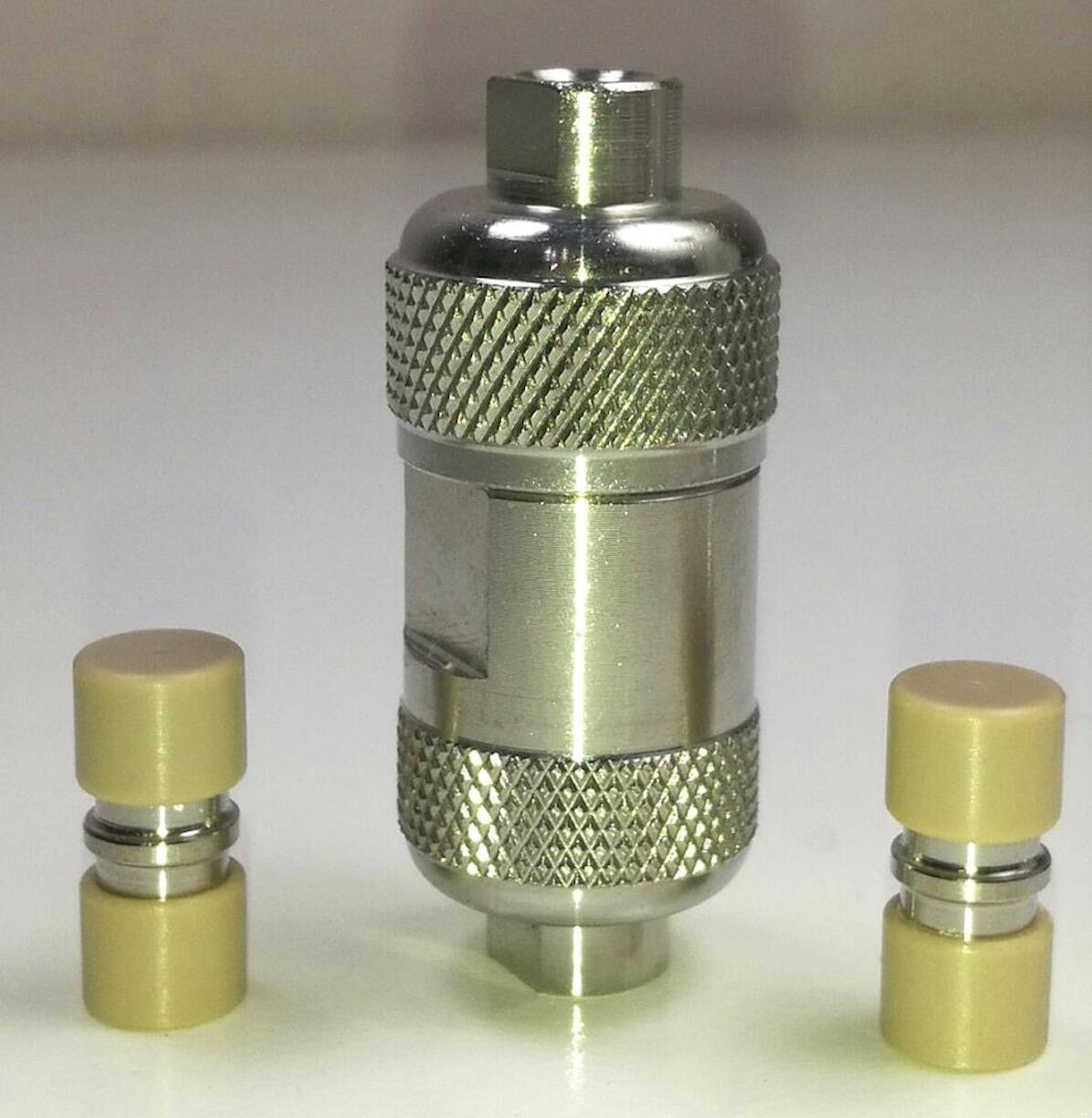
استخراج فاز جامد برای آزمایش غذا
استخراج فاز جامد (SPE) یک تکنیک تحلیلی مهم در آزمایش مواد غذایی مدرن را نمایان میدهد، که رویکرد پیشرفتهای برای آمادهسازی نمونه و جدا کردن آلودگیها ارائه میدهد. این روش با گذراندن نمونه مایع از ماده جاذب جامد که به طور انتخابی ترکیبات خاصی را نگهداری میکند و دیگری را عبور میدهد، عمل میکند. فرآیند معمولاً شامل چهار مرحله اصلی است: شرایطبخشی به جاذب، بارگذاری نمونه، شستشو برای حذف مداخلات و الوتاس ترکیبات هدف. در کاربردهای آزمایش مواد غذایی، SPE برای تشخیص و اندازهگیری انواع مواد مختلف، از جمله باقیماندههای سموم گیاهان، میکوتوксینها، آنتیبیوتیکها و سایر آلودگیهای غذایی، ارزشمند است. این فناوری از مواد جاذب مختلفی مثل ترکیبات مبتنی بر سیلیکا، مواد چندپلیمری و پلیمرهای چاپ شده مولکولی استفاده میکند، هر کدام برای هدفگیری تحلیلیهای خاص طراحی شدهاند. سیستمهای پیشرفته SPE حالا قابلیتهای خودکارسازی را در بر میگیرند، که از کاهش دستیابی دستی و بهبود تکرارپذیری حمایت میکند. این روش در سراسر جهان در آزمایشگاههای ایمنی غذا به عنوان ابزاری ضروری شناخته شده است، که کارایی تمیزکاری بالا و توانایی متمرکز کردن تحلیلیهای ردیفی از ماتریسهای غذایی پیچیده را ارائه میدهد. چندوجهی بودن SPE امکان تجزیه و تحلیل همراه با تجزیه و تحلیل چند ردیفی را فراهم میکند، که آن را به ابزاری ضروری در آزمایشهای مربوط به رعایت مقررات و روالهای کنترل کیفیت در صنعت غذا تبدیل میکند.